Posterior Pelvic Bone Anatomy
There are 3 hip bones. These three bones are also known as the innominate bones pelvic bones or coxal bones.
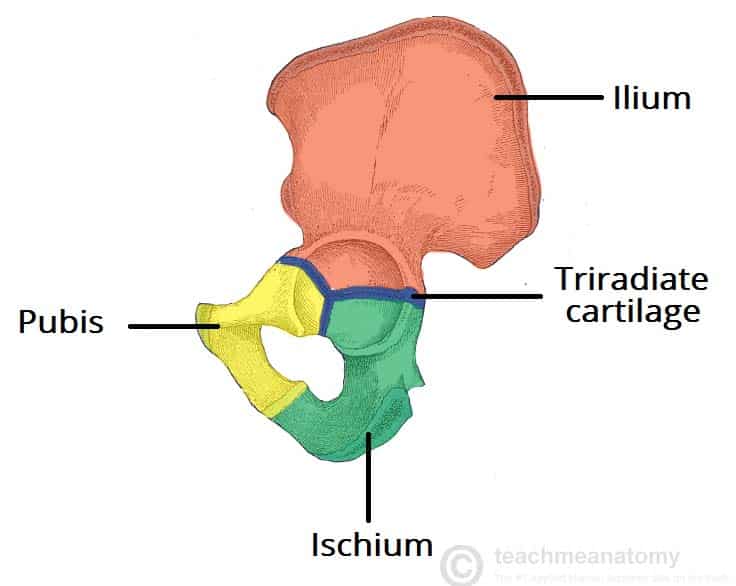
The Hip Bone Ilium Ischium Pubis Teachmeanatomy
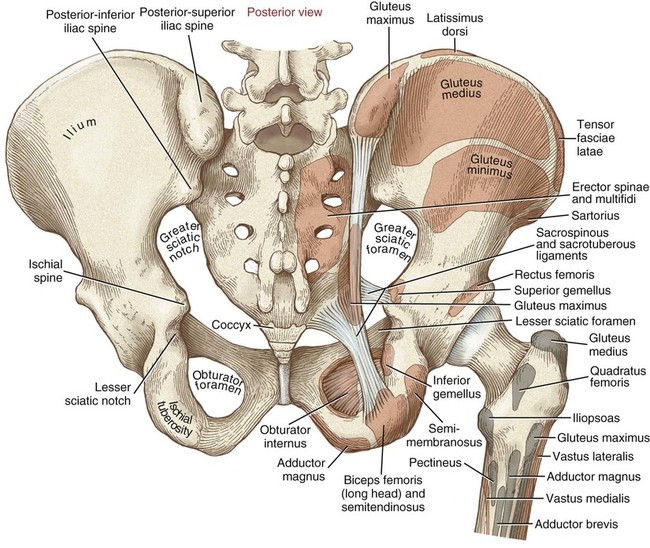
Structure And Function Of The Hip Musculoskeletal Key

Pelvic Fractures Orthoinfo Aaos
It consists of three bones.

Posterior pelvic bone anatomy. Anatomy of the femur. As it descends towards the knee it is separated from the longest tubular bone or shaft by the femoral neck. The femur or thighbone is the longest and strongest bone in the human skeleton.
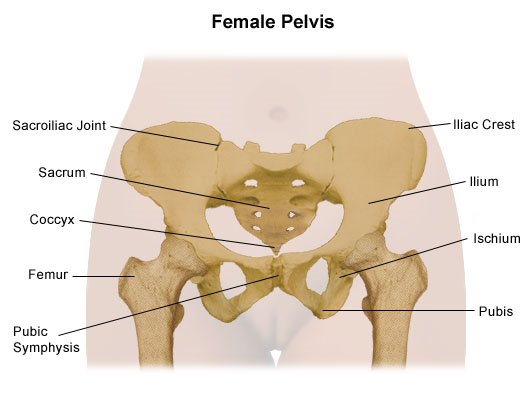
The pelvis is the lower portion of the trunk located between the abdomen and the lower limbs. The pelvic girdle also known as the os coxae Latin for bone of the hip consists of the fused bones identified individually as the ilium ischium and pubis. The serratus posterior superior muscle.
The vertebral column of the lower back includes the five lumbar vertebrae the sacrum and the coccyx. In this article we shall look at the attachments actions and innervation of the muscles in the posterior compartment of the leg. The ilium ischium and the pubis.
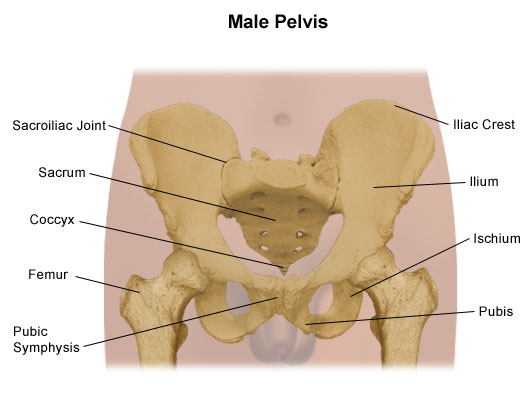
The hip is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur the leg bone fits into the pelvis. The ilium is a flat curved bone and bears the iliac crest superiorly. Bones of the Pelvis and Lower Back.
The pelvic girdle consists of the os coxae or hip bones. They develop separately from each other and in children are connected only by cartilageHowever they completely fuse during puberty to comprise the complex and compact hip bone. So lets start with the anteroinferior wall formed by the bodies and rami of pubic bones and the pubic symphysis.
The change in the shape of the pelvic floor during. These three bones fuse at a cup-shaped concavity called the acetabulum which articulates with the head of the femur to form the hip joint. The pelvic skeleton is formed posteriorly in the area of the back by the sacrum and the coccyx and laterally and anteriorly forward and to the sides by a pair of hip bonesEach hip bone consists of 3 sections ilium ischium and pubisDuring childhood these sections are separate bones joined by the triradiate cartilageDuring puberty they fuse together to form a single bone.
The hip bone is an irregularly shaped bone also known as the pelvic girdle. They are innervated by the tibial nerve a terminal branch of the sciatic nerve. Together these muscles comprise the intermediate layer of the extrinsic musculature of the back.
The right and left hip bones also converge anteriorly to attach to each other. These bones are also called coxal bones innominate bones or pelvic bones. The ring of this girdle is closed in the anterior by the pubic symphysis between the left and right pubic bones and in the posterior between the left and right ilia and the sacrum at the sacroiliac joints.
In the platypelloid the baby will engage from Left Occiput Transverse before they can engage in pregnancy or in labor because of this pelvic shape. The anterior and posterior superior iliac spines are on either end of the iliac crest with the anterior and posterior inferior iliac spines below them. The serratus posterior muscles extend obliquely from the vertebral column to the rib cage.
It consists of two lobes that arise from distinct parts of embryonic tissue. Anatomy Next provides anatomy learning tools for students and teachers. As its name implies it contains organs lying more posterior in the.
The pelvic girdle hip girdle is formed by a single bone the hip bone or coxal bone coxal hip which serves as the attachment point for each lower limb. The hip bone os coxae innominate bone pelvic bone or coxal bone is a large flat bone constricted in the center and expanded above and belowIn some vertebrates including humans before puberty it is composed of three parts. Whether youre exercising or just standing around the chronic position of your pelvis matters a great deal to your spinal alignment and your low.
Prepares you to excel in anatomy exam by providing important questions on all topics Head neck Thorax Abdomen Pelvis Perineum Upper limb lower limb and neuroanatomy. Each pubic bone has three parts. When the two hip bones are combined with the sacrum and coccyx of the axial skeleton they are referred to as the pelvisThe right and left hip bones also converge anteriorly to attach to each other at the pubic symphysis Figure 831.
The pelvic cavity also has an anteroinferior wall two lateral walls and a posterior wall. The pelvic girdle hip girdle is formed by a single bone the hip bone or coxal bone coxal hip which serves as the attachment point for each lower limbEach hip bone in turn is firmly joined to the axial skeleton via its attachment to the sacrum of the vertebral column. The design of the female pelvis is in such a way that it provides adequate space for the baby to develop and go through the birth canal of the female pelvis.
The right and left hip bones also converge anteriorly to attach to each other. The two hip bones also called coxal bones or os coxae are together called the pelvic girdle hip girdle and serve as the attachment point for each lower limb. Posterior pelvic tilt is a movement in which the front of the pelvis rises and the back of the pelvis drops while the pelvis rotates upwards.
Ventrally toward the pubic bone 38. They start out as three separate bones ilium ischium and. Hip bones anatomy notes illustrations mnemonics and free video tutorial.
The ilium ischium and pubis that fuse together in adolescence to create the butterfly shaped wings of the hips on each side of the body. Each hip bone in turn is firmly joined to the axial skeleton via its attachment to the sacrum of the vertebral column. The posterior wall of the EAS is shorter in its cranio-caudal extent than the anterior wall.
The pelvic cavity contains most of the urogenital system as well as the rectum. The serratus posterior inferior muscle. In the Android pelvis the baby must be LOA for optimal engagement.
A body and a superior and inferior ramus. Collectively the muscles in this area plantarflex and invert the foot. The two hip bones join at the pubic symphysis and together with the sacrum and coccyx the pelvic part of the spine comprise the.
A birth stool posterior pelvic tilt and standing and leaning over a dresser feels right. The posterior leg is the largest of the three compartments. Anatomy The bony pelvis.
The smaller of the two main cavities is called the dorsal cavity. There are some structural differences between male and female pelvic bone anatomy. The bony pelvis is made up of two pelvic bones the sacrum and the coccyx.
The inner surface of the bone is smooth and has a sharp crest at its base the arcuate line running from the sacroiliac joint to the iliopectineal eminence. Useful for students of MBBS BDS BPT and Allied health sciences. The bones of the pelvis and lower back work together to support the bodys weight anchor the abdominal and hip muscles and protect the delicate vital organs of the vertebral and abdominopelvic cavities.
As the clear picture of. The pituitary gland is cradled within the sellaturcica of the sphenoid bone of the skull. The posterior pituitary neurohypophysis is neural tissue whereas the anterior pituitary also known as the adenohypophysis is glandular tissue that develops from the primitive digestive tract.
Ilium ischium and pubis. It extends from the hip to the knee joint. The femoral head is the distal upper end of the femur that inserts into the acetabulum of the hip joint.
In fact during pelvic floor contraction the coccyx moves ventrally and cranially. The pelviss frame is made up of the bones of the pelvis which connect the axial skeleton to the femurs and therefore acts in weight bearing of the upper body. The serratus posterior muscles are two paired muscles located in the upper and lower back.
The pelvic cavity is bounded cranially by the abdominal cavity dorsally by the sacrum and laterally by the pelvis. Each pelvic bone hip bone is made by the combination three bones namely the ilium pubis and ischium.
Pelvis Problems Johns Hopkins Medicine
/3d-illustration-of-hip-skeleton-1179119356-7d7fef18c4774d43b59f8b1ce239a620.jpg)
Pubis Anatomy Function And Treatment
Anatomy Of The Pelvic Girdle Physiopedia
Pelvis Problems Johns Hopkins Medicine
1

Clinically Applied Anatomy Of The Pelvis Sciencedirect

Rear View Of Male Pelvis Hip Leg Bones And Ligaments Labeled On A Black Background Stocktrek Images

Pelvis And Hip Joint Knowledge Amboss
Comments
Post a Comment